Reduced hnRNPA3 increases C9orf72 repeat RNA levels and dipeptide-repeat protein deposition
EMBO Reports, published online 26.07.2016
| Authors/Editors: |
Kohji Mori Yoshihiro Nihei Thomas Arzberger Qihui Zhou Ian R Mackenzie Andreas Hermann Frank Hanisch German Consortium for Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration Bavarian Brain Banking Alliance Frits Kamp Brigitte Nuscher Denise Orozco Dieter Edbauer Christian Haass |
|---|---|
| Publication Date: | 2016 |
| Type of Publication: | Journal Article |
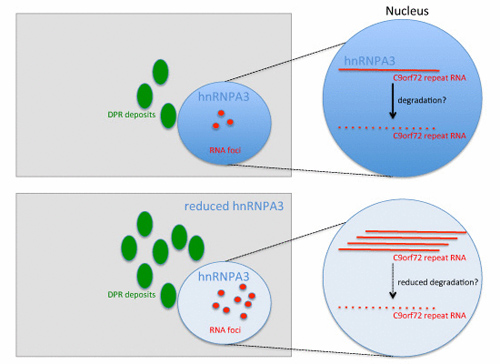
FTLD/ALS‐associated repeat expansions in C9orf72 are translated into dipeptide repeat proteins. Reduction of repeat‐binding hnRNPA3 increases levels of the repeat RNA and enhances production of dipeptide repeat proteins and RNA foci.
Highlights:
- Reduction of nuclear hnRNPA3 increases levels of the C9orf72 repeat RNA.
- Reduction of nuclear hnRNPA3 increases RNA foci formation and enhances generation and deposition of dipeptide repeat proteins.
- Reduced nuclear hnRNPA3 in the hippocampus of patients with extended C9orf72 repeats correlates with increased dipeptide repeat protein deposition.
Intronic hexanucleotide (G4C2) repeat expansions in C9orf72 are genetically associated with frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD) and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). The repeat RNA accumulates within RNA foci but is also translated into disease characterizing dipeptide repeat proteins (DPR). Repeat-dependent toxicity may affect nuclear import. hnRNPA3 is a heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein, which specifically binds to the G4C2 repeat RNA. We now report that a reduction of nuclear hnRNPA3 leads to an increase of the repeat RNA as well as DPR production and deposition in primary neurons and a novel tissue culture model that reproduces features of the C9orf72 pathology. In fibroblasts derived from patients carrying extended C9orf72 repeats, nuclear RNA foci accumulated upon reduction of hnRNPA3. Neurons in the hippocampus of C9orf72 patients are frequently devoid of hnRNPA3. Reduced nuclear hnRNPA3 in the hippocampus of patients with extended C9orf72 repeats correlates with increased DPR deposition. Thus, reduced hnRNPA3 expression in C9orf72 cases leads to increased levels of the repeat RNA as well as enhanced production and deposition of DPR proteins and RNA foci.